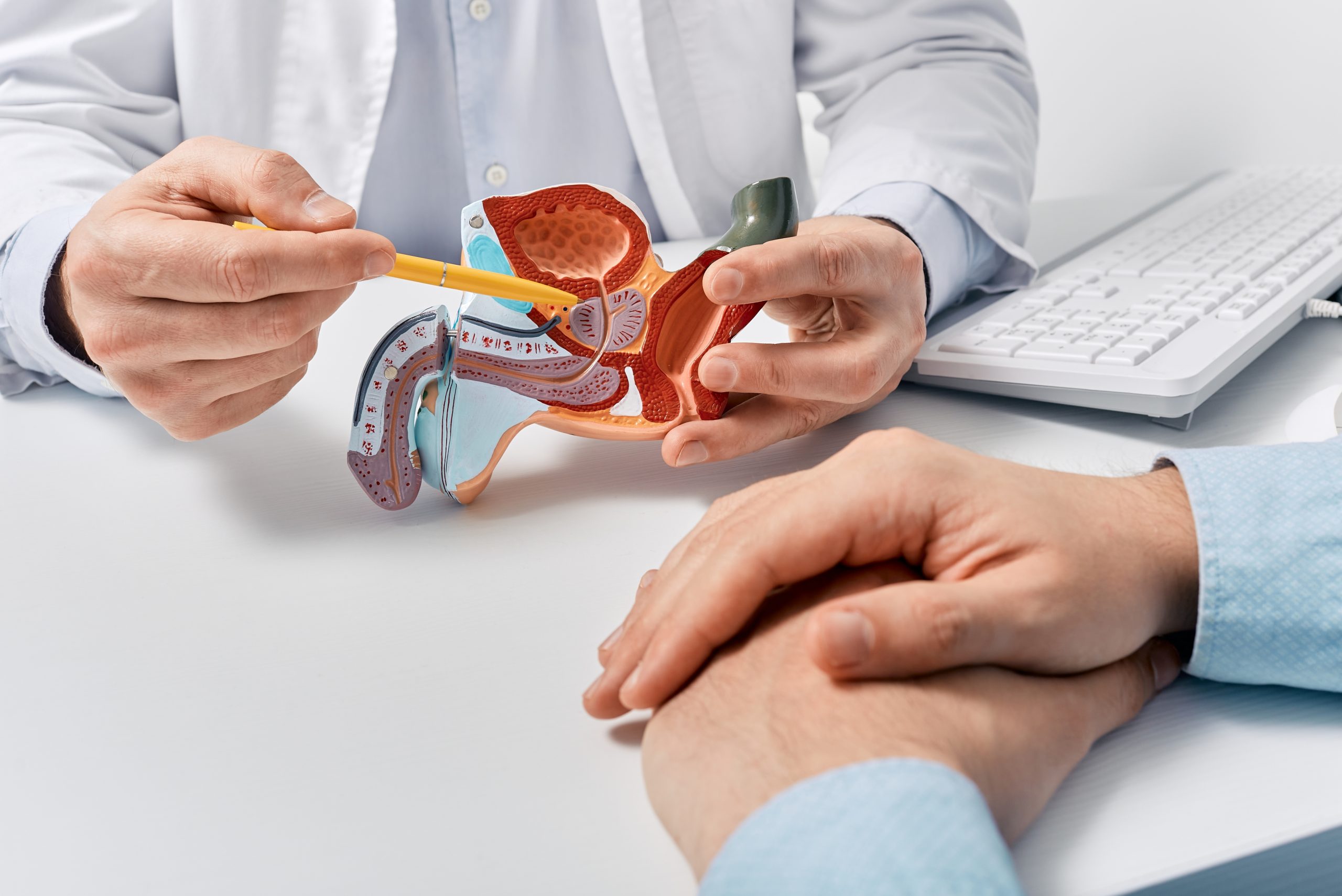
As men age, their prostate gland undergoes changes that can have an impact on their overall prostate health. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland that plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. Understanding how age affects the prostate can help men make informed decisions about their health and take appropriate steps to maintain prostate health. In this article, we’ll explore the impact of age on prostate health.
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
One of the most common prostate conditions that occur with age is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, which can cause urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, and difficulty starting or stopping urination. BPH is a natural part of the aging process and affects a significant number of men over the age of 50. While BPH is not a life-threatening condition, it can significantly impact quality of life. Regular prostate screenings and discussions with a healthcare provider can help monitor and manage BPH symptoms.
- Prostate Cancer
Age is a significant risk factor for prostate cancer. The likelihood of developing prostate cancer increases with age, especially after the age of 50. It is important for men to be aware of the symptoms of prostate cancer, which may include urinary changes, blood in the urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, and pelvic pain. Early detection through regular prostate screenings, such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test and digital rectal examination (DRE), is crucial for detecting and treating prostate cancer at its early stages when it is most treatable.
- Prostatitis
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland, which can cause pain and discomfort in the pelvic area. While prostatitis can affect men of all ages, it is more common in middle-aged and older men. Symptoms of prostatitis may include pain during urination, frequent urination, and pelvic pain. Treatment for prostatitis often involves medication, lifestyle changes, and other therapies to manage symptoms and reduce inflammation.
- Hormonal Changes
With age, there can be hormonal changes that affect prostate health. The hormone testosterone plays a role in prostate function and growth. As men age, testosterone levels may gradually decline, which can influence prostate health. Hormonal changes can contribute to the development of conditions such as BPH and prostate cancer. It is important to discuss any concerns about hormonal changes with a healthcare provider who can provide guidance and appropriate treatment options.
- Regular Prostate Screenings
Regular prostate screenings are essential for maintaining prostate health as men age. The American Cancer Society recommends that men discuss prostate cancer screening with their healthcare provider starting at age 50, or earlier for those with risk factors or a family history of prostate cancer. Prostate screenings typically include a PSA blood test and a digital rectal examination. These screenings can help detect potential issues early and allow for appropriate intervention and treatment.
- Lifestyle Factors
While age-related changes to the prostate are natural, certain lifestyle factors can help support prostate health. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and adopting a nutritious diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can contribute to overall prostate health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help reduce the risk of developing prostate-related conditions.
In conclusion, age has a significant impact on prostate health. With advancing age, men should be proactive in monitoring their prostate health through regular screenings and discussions with their healthcare providers. Understanding the potential changes that occur with age can empower men to take steps to maintain their prostate health and overall well-being.