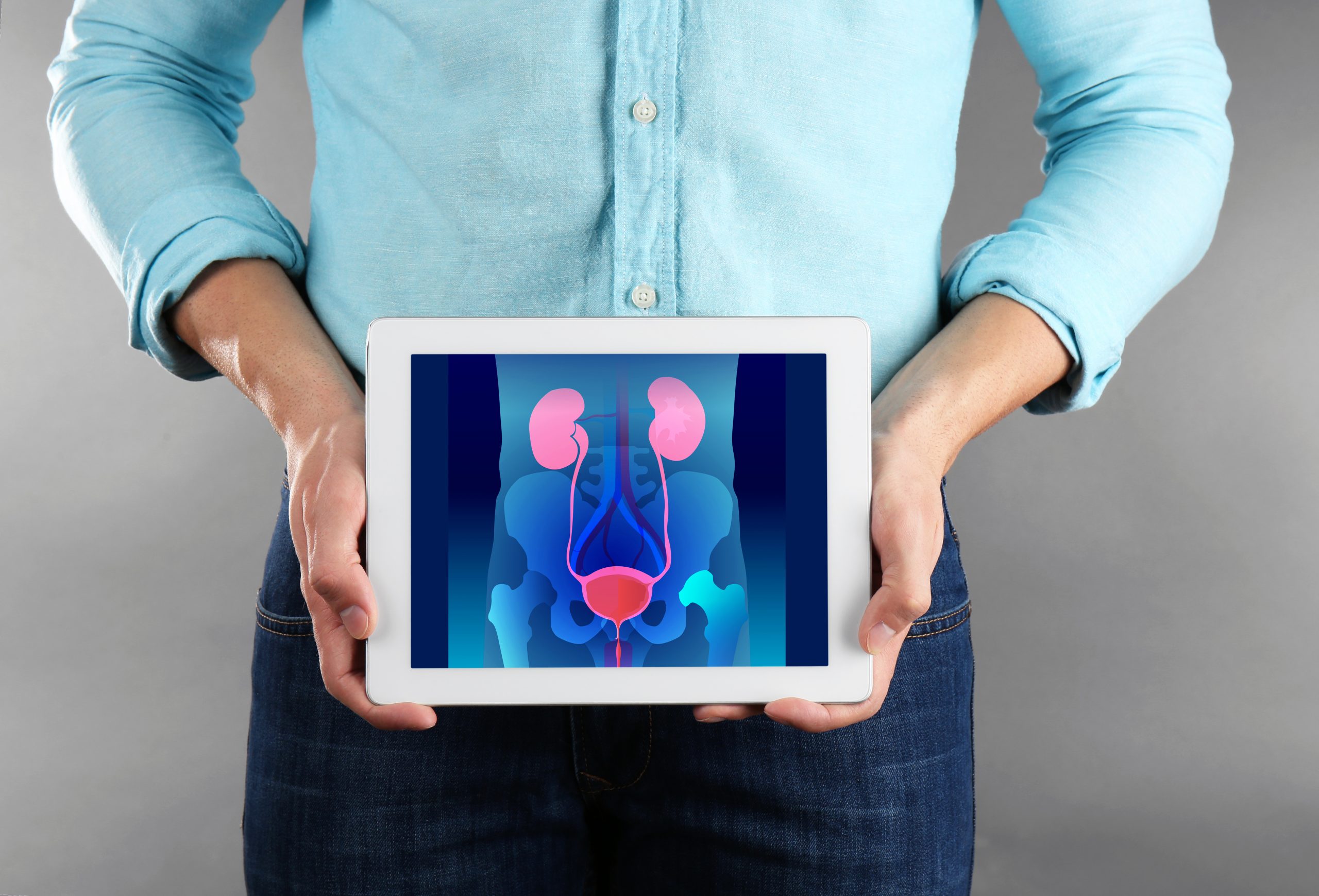
The prostate and kidneys are both vital organs that play crucial roles in maintaining overall health and well-being. While they serve different functions, there is a significant connection between prostate health and kidney function. In this article, we explore the connection between these two important aspects of men’s health.
- Prostate and Urinary System: The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system, situated just below the bladder. It surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. The kidneys, on the other hand, are responsible for filtering waste products and excess fluid from the blood, producing urine, and maintaining the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance. The prostate and kidneys are both involved in the urinary system, and any issues in one organ can affect the other.
- Urinary Symptoms: Conditions that affect the prostate, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer, can lead to urinary symptoms that affect kidney function. An enlarged prostate can compress the urethra, obstructing the flow of urine and causing urinary retention. This can lead to complications, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney stones. Chronic urinary obstruction or infections can put additional strain on the kidneys, potentially impacting their function over time.
- Kidney Stones: Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause intense pain and discomfort. Certain factors, including an enlarged prostate, can increase the risk of developing kidney stones. An enlarged prostate can obstruct the flow of urine, leading to urine stagnation in the urinary tract. Stagnant urine provides an environment conducive to the formation of kidney stones. Managing prostate health can help reduce the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Urinary tract infections can occur when bacteria enter the urinary system and multiply, causing an infection. Prostate conditions, such as BPH, can contribute to the development of UTIs. An enlarged prostate can obstruct the urinary flow, leading to incomplete emptying of the bladder. Residual urine in the bladder can increase the risk of bacterial growth and infections. UTIs, if left untreated, can potentially spread to the kidneys and cause more severe complications.
- Prostate Cancer and Kidney Health: Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men. In advanced stages, prostate cancer can spread to other parts of the body, including the kidneys. When cancer cells metastasize to the kidneys, they can affect kidney function and compromise overall renal health. Regular monitoring of prostate health, early detection, and appropriate treatment are important in preventing the spread of prostate cancer to the kidneys and preserving kidney function.
- Medications and Kidney Function: Medications used to manage prostate conditions, such as BPH, can have an impact on kidney function. Some medications, including alpha-blockers or 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, can affect blood pressure or alter fluid balance in the body. It’s important for individuals with prostate conditions to discuss the potential effects of medications on kidney function with their healthcare provider.
- Overall Health and Lifestyle Factors: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is beneficial for both prostate health and kidney function. Factors such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper hydration support overall health and can reduce the risk of prostate and kidney problems. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients and antioxidants that support both prostate health and kidney function.
In conclusion, there is a clear connection between prostate health and kidney function. Issues affecting the prostate can impact urinary flow and increase the risk of complications that affect kidney health. It’s important for men to prioritize regular check-ups, discuss any concerns