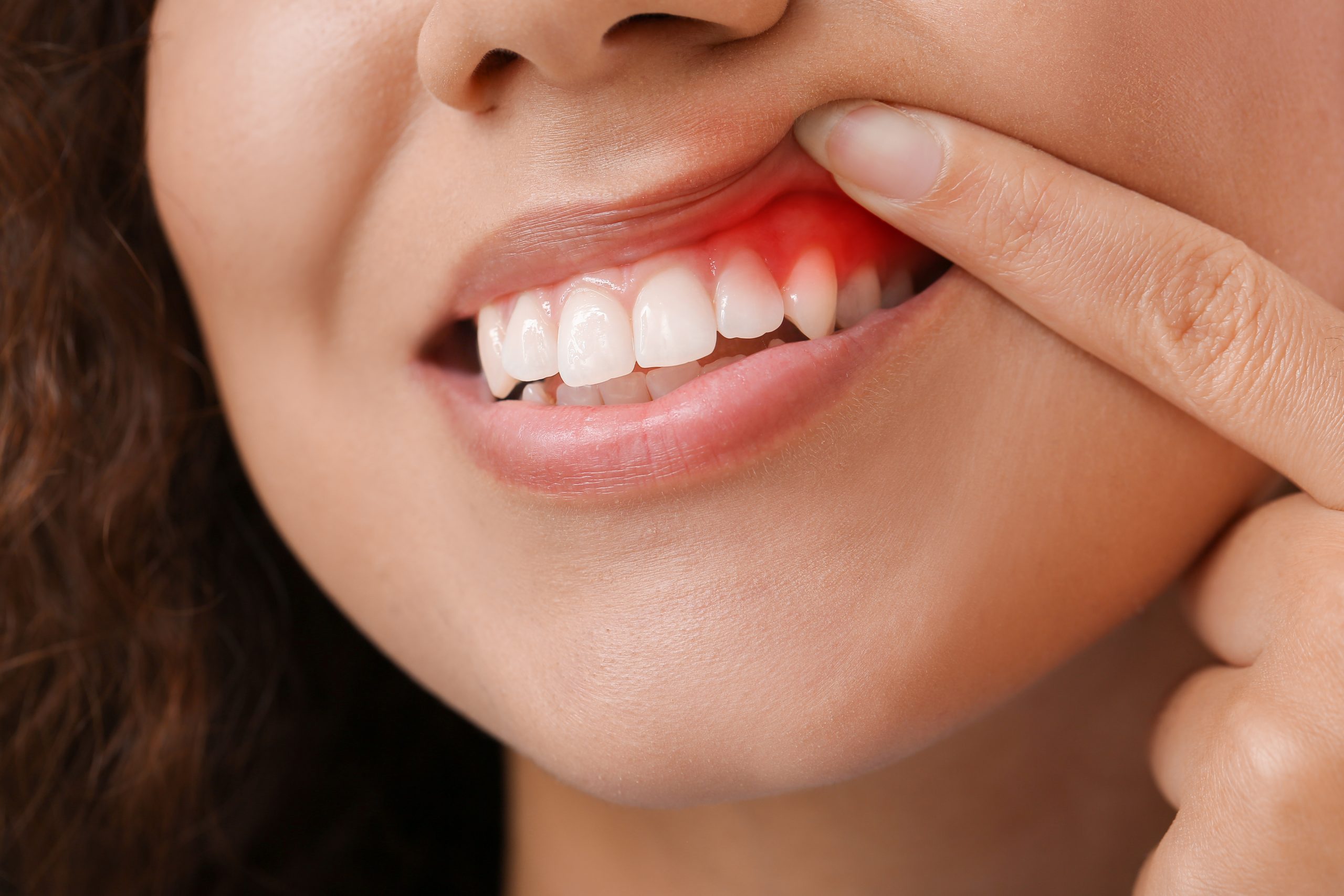
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It starts with inflammation of the gums and, if left untreated, can progress to more severe stages, leading to tooth loss and other oral health problems. Managing gum disease is crucial for maintaining healthy gums and preventing further damage. In this article, we explore tips on how to manage gum disease effectively.
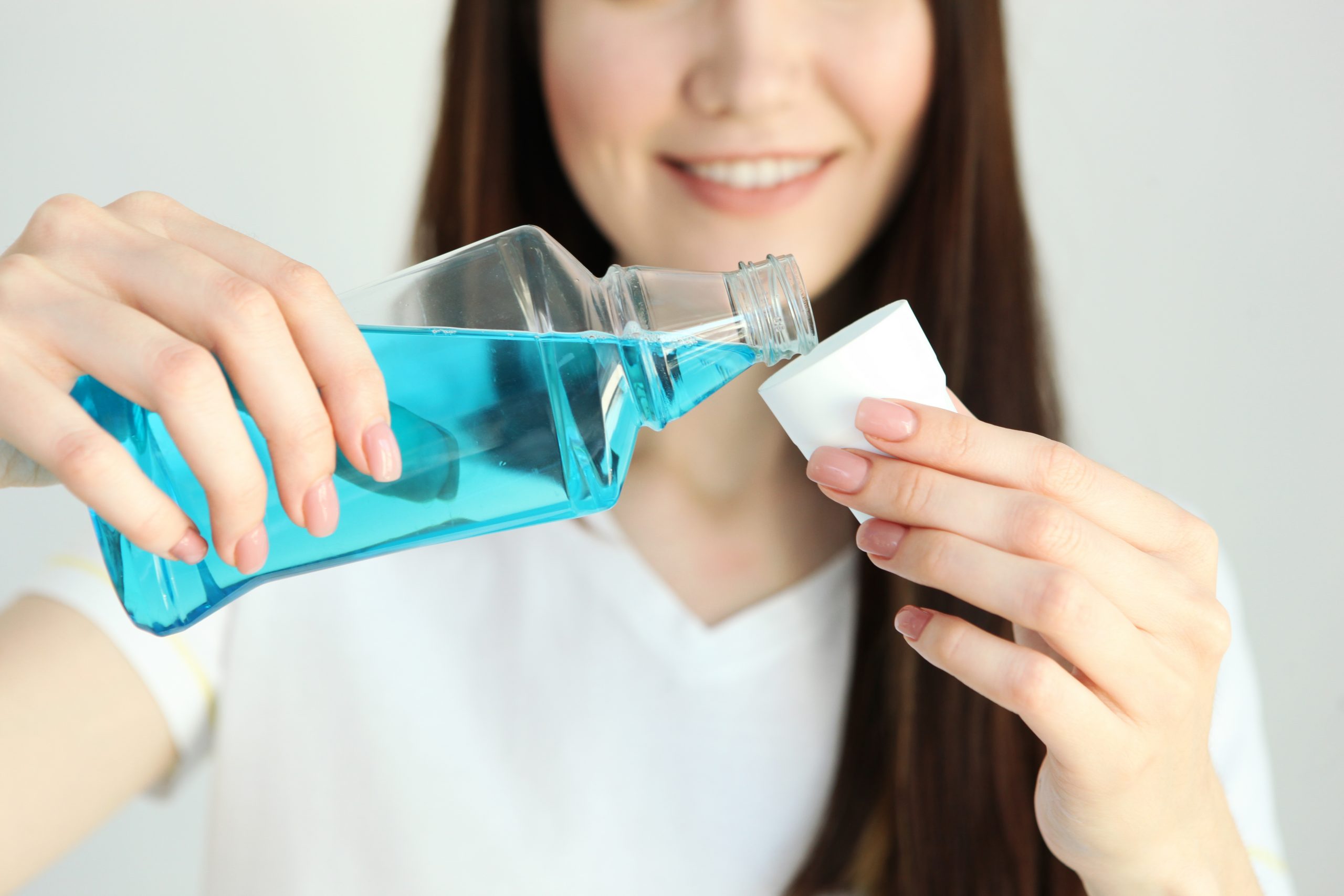
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine is key to managing gum disease. Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Pay special attention to the gumline, where bacteria tend to accumulate. Additionally, floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline. Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to further reduce bacteria in your mouth.
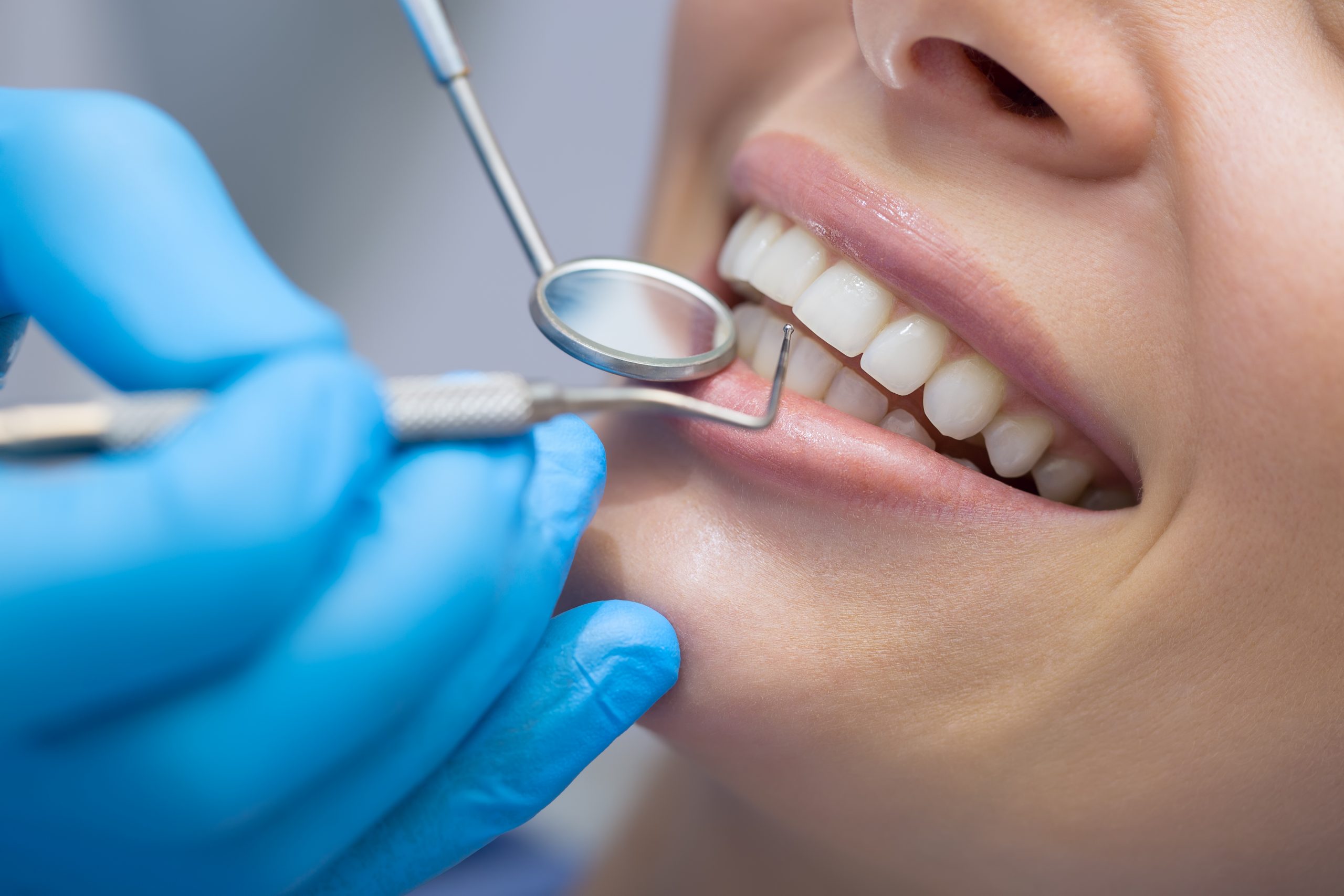
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Regular dental check-ups are crucial for managing gum disease. Your dentist can assess the health of your gums, perform professional cleanings, and identify any signs of gum disease or other oral health issues. Schedule dental appointments every six months or as recommended by your dentist. These visits allow for early detection and intervention, preventing the progression of gum disease.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking and the use of tobacco products can significantly worsen gum disease. Nicotine and other harmful chemicals in tobacco products impair blood flow to the gums, making it harder for your body to fight off infection and repair damaged tissues. Quitting smoking can improve the health of your gums and enhance your overall oral health. Seek support from healthcare professionals or smoking cessation programs to help you quit successfully.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet plays a vital role in managing gum disease. Include foods rich in vitamins C and E, as well as antioxidants, which help support gum health and boost the immune system. Avoid sugary and starchy foods that can contribute to plaque buildup and bacterial growth. A well-balanced diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for gum tissue repair and maintenance.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections, including gum disease. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as engaging in regular physical exercise, practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation, and participating in activities you enjoy. Prioritizing self-care and stress management can have a positive impact on your overall health, including your gum health.
- Use an Antibacterial Mouthwash: Consider using an antibacterial mouthwash recommended by your dentist or periodontist. An antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce the bacterial load in your mouth, inhibit plaque formation, and manage gum disease. Use the mouthwash as directed, typically after brushing and flossing, to enhance your oral hygiene routine.
- Maintain Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Healthy lifestyle habits contribute to overall well-being, including gum health. Get enough sleep to support your immune system’s function and allow your body to repair and regenerate tissues. Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol intake can contribute to gum inflammation. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water to promote saliva production, which helps neutralize acids and wash away bacteria.
- Consider Professional Treatments: In more advanced stages of gum disease, professional treatments may be necessary to manage the condition effectively. Scaling and root planing, also known as deep cleaning, can remove plaque and tartar buildup from below the gumline. Your dentist or periodontist may also recommend other treatments, such as antibiotics, periodontal surgery, or laser therapy, depending on the severity of your gum disease.
Remember, early detection and intervention are crucial in managing gum disease effectively. If you